Node based analysis with latent space model
The node-based latent space model approach calculates latent positions of the networks, and use them in the SEM analysis along with non-network variables.
Simulated Data Example
To begin with, a random simulated dataset can be used to demonstrate the usage of the node-based network statistics approach. The code below generate a simulated network net with four non-network covariates x1 - x4 which loads on two latent variables lv1, lv2.
set.seed(10)
nsamp = 50
net <- ifelse(matrix(rnorm(nsamp^2), nsamp, nsamp) > 1, 1, 0)
mean(net) # density of simulated network
lv1 <- rnorm(nsamp)
lv2 <- rnorm(nsamp)
nonnet <- data.frame(x1 = lv1*0.5 + rnorm(nsamp),
x2 = lv1*0.8 + rnorm(nsamp),
x3 = lv2*0.5 + rnorm(nsamp),
x4 = lv2*0.8 + rnorm(nsamp))With the simulated data, we can define a model string with lavaan syntax that specifies the measurement model as well as the relationship between the network and the non-network variables. In this case, we are using net as a mediator between the two latent variables. Since data are generated randomly, the effects should be small overall.
model <-'
lv1 =~ x1 + x2
lv2 =~ x3 + x4
net ~ lv2
lv1 ~ net + lv2
'Arguments passed to the sem.net.lsm function includes the model, the dataset, and the number of latent dimensions. Note that data here should be a list with two elements, one being the named list of all network variables and one being the dataframe containing non-network variables. A summary function can be used to look at the output, and the function path.networksem can be used to look at mediation effects across the two latent dimensions.
data = list(network = list(net = net), nonnetwork = nonnet)
set.seed(100)
res <- sem.net.lsm(model = model, data = data, latent.dim = 2)
summary(res)
path.networksem(res, 'lv2', c('net.Z1', 'net.Z2'), 'lv1') The output looks like the following.
> summary(res)
Model Fit InformationSEM Test statistics: 3.771276 on 6 df with p-value: 0.7075962
NOTE: It is not certain whether it is appropriate to use latentnet's BIC to select latent space dimension, whether or not to include actor-specific random effects, and to compare clustered models with the unclustered model.
network 1 LSM BIC: 2242.696
========================================
========================================
The SEM output:
lavaan 0.6.15 ended normally after 117 iterations
Estimator ML
Optimization method NLMINB
Number of model parameters 15
Number of observations 50
Model Test User Model:
Test statistic 3.771
Degrees of freedom 6
P-value (Chi-square) 0.708
Model Test Baseline Model:
Test statistic 34.438
Degrees of freedom 15
P-value 0.003
User Model versus Baseline Model:
Comparative Fit Index (CFI) 1.000
Tucker-Lewis Index (TLI) 1.287
Loglikelihood and Information Criteria:
Loglikelihood user model (H0) -434.447
Loglikelihood unrestricted model (H1) -432.561
Akaike (AIC) 898.893
Bayesian (BIC) 927.574
Sample-size adjusted Bayesian (SABIC) 880.491
Root Mean Square Error of Approximation:
RMSEA 0.000
90 Percent confidence interval - lower 0.000
90 Percent confidence interval - upper 0.138
P-value H_0: RMSEA <= 0.050 0.765
P-value H_0: RMSEA >= 0.080 0.165
Standardized Root Mean Square Residual:
SRMR 0.062
Parameter Estimates:
Standard errors Standard
Information Expected
Information saturated (h1) model Structured
Latent Variables:
Estimate Std.Err z-value P(>|z|)
lv2 =~
x4 1.000
x3 4.622 6.418 0.720 0.471
lv1 =~
x2 1.000
x1 -0.088 0.271 -0.326 0.744
Regressions:
Estimate Std.Err z-value P(>|z|)
lv1 ~
lv2 -0.984 0.432 -2.279 0.023
net.Z1 ~
lv2 -0.159 0.207 -0.765 0.444
net.Z2 ~
lv2 0.208 0.257 0.809 0.418
lv1 ~
net.Z1 -0.215 0.169 -1.277 0.202
net.Z2 0.255 0.138 1.850 0.064
Variances:
Estimate Std.Err z-value P(>|z|)
.x4 1.947 0.425 4.581 0.000
.x3 -1.587 3.655 -0.434 0.664
.x2 2.927 6.822 0.429 0.668
.x1 1.345 0.274 4.906 0.000
.net.Z1 0.624 0.124 5.012 0.000
.net.Z2 0.950 0.189 5.013 0.000
lv2 0.139 0.227 0.612 0.541
.lv1 -1.984 6.796 -0.292 0.770
The LSM output:
==========================
Summary of model fit
==========================
Formula: network::network(data$network[[latent.network[i]]]) ~ euclidean(d = latent.dim)
<environment: 0x7fc43202a550>
Attribute: edges
Model: Bernoulli
MCMC sample of size 4000, draws are 10 iterations apart, after burnin of 10000 iterations.
Covariate coefficients posterior means:
Estimate 2.5% 97.5% 2*min(Pr(>0),Pr(<0))
(Intercept) -0.18777 -0.42332 0.05 0.1175
Overall BIC: 2242.696
Likelihood BIC: 2107.714
Latent space/clustering BIC: 134.9814
Covariate coefficients MKL:
Estimate
(Intercept) -0.8639125
> path.networksem(res, 'lv2', c('net.Z1', 'net.Z2'), 'lv1')
predictor mediator outcome apath bpath indirect
1 lv2 net.Z1 lv1 -0.1587188 -0.2154100 0.03418961
2 lv2 net.Z2 lv1 0.2081154 0.2547222 0.05301162
indirect_se indirect_z
1 0.04030792 0.8482108
2 0.05368411 0.9874733Empirical Data Example
We fit the same model on the friendship and WeChat networks from the network statistics approach using the LSM approach. Under this approach, the latent positions take the roles of the network statistics but the model string can stay the same.
model <-'
Extroversion =~ personality1 + personality6
+ personality11 + personality16
Conscientiousness =~ personality2 + personality7
+ personality12 + personality17
Neuroticism =~ personality3 + personality8
+ personality13 + personality18
Openness =~ personality4 + personality9
+ personality14 + personality19
Agreeableness =~ personality5 + personality10 +
personality15 + personality20
Happiness =~ happy1 + happy2 + happy3 + happy4
friends ~ Extroversion + Conscientiousness + Neuroticism +
Openness + Agreeableness
Happiness ~ friends + wechat
'To fit the model, the sem.net.lsm() function is used. The argument latent.dim should be used to denote the number of latent dimensions to be used in estimating the LSM. A random seed can be set to ensure reproduction of the results, and the argument data.scale = T is used so the scale of the latent positions and the non-network variables are not too different.
data = list(network=network, nonnetwork=non_network)
set.seed(100)
res <- sem.net.lsm(model=model,data=data, latent.dim = 2, data.rescale = T)For SEM with latent positions, the estimation is again a two-stage process. First, a latent space model with no covariates is used to estimate latent positions through the latentnet R package. The resulting latent positions are then be extracted and compiled into the same dataset as the non-network variables such as the Big Five personality items and the happiness score items, which are then inputted into lavaan to be estimated in the SEM framework. We could again use res$data to access the restructured data with latent positions, and res$model to access the modified model string. The output of sem.net.lsm() has two components in res$estimates - res$estimates$sem.es for lavaan SEM results and res$estimates$lsm.es for latentnet LSM results.
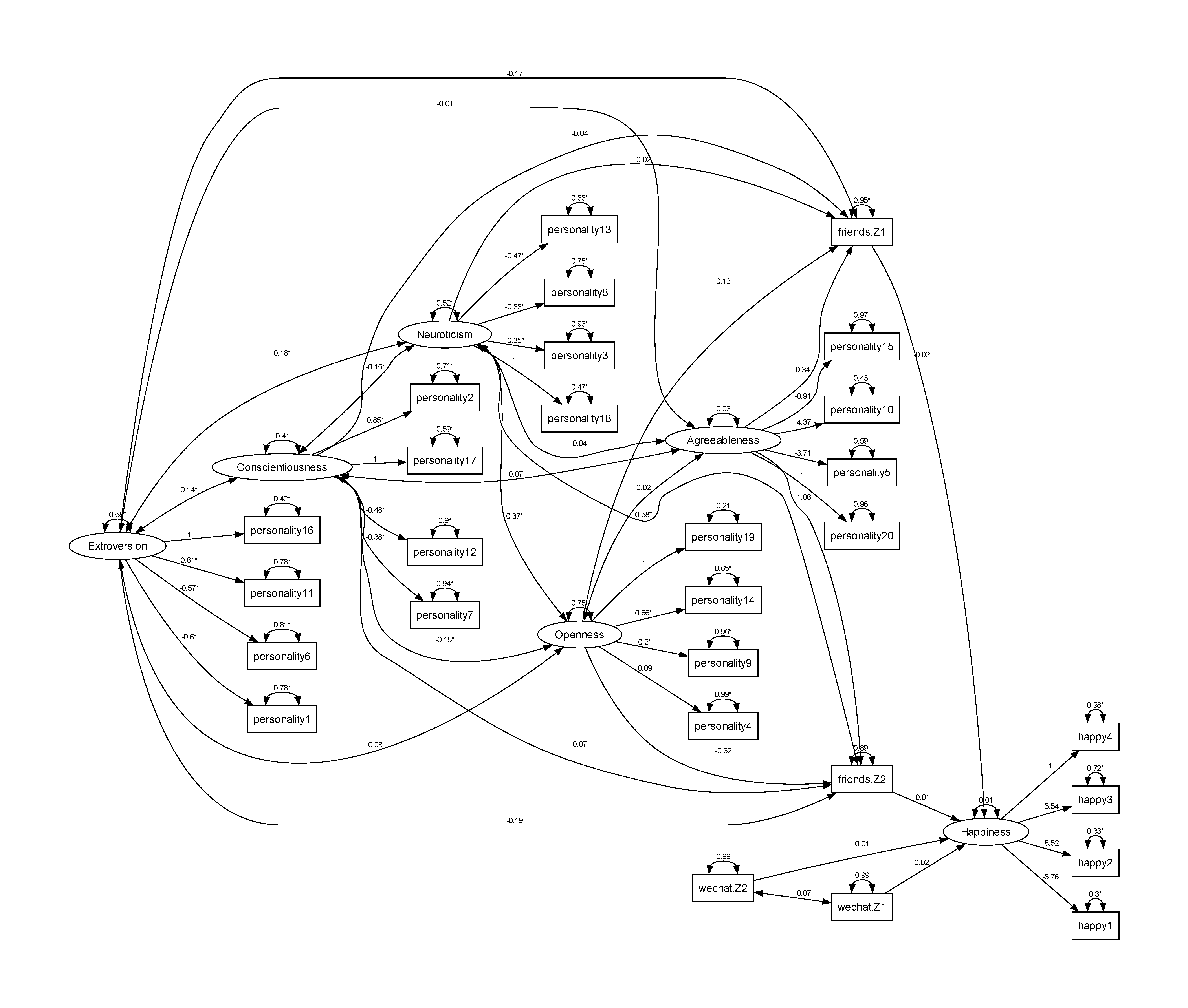
The output of the analysis is given below:
lavaan 0.6.15 ended normally after 195 iterations
Estimator ML
Optimization method NLMINB
Number of model parameters 74
Number of observations 165
Model Test User Model:
Test statistic 947.953
Degrees of freedom 329
P-value (Chi-square) 0.000
Model Test Baseline Model:
Test statistic 1448.277
Degrees of freedom 377
P-value 0.000
User Model versus Baseline Model:
Comparative Fit Index (CFI) 0.422
Tucker-Lewis Index (TLI) 0.338
Loglikelihood and Information Criteria:
Loglikelihood user model (H0) -6642.329
Loglikelihood unrestricted model (H1) -6168.353
Akaike (AIC) 13432.658
Bayesian (BIC) 13662.498
Sample-size adjusted Bayesian (SABIC) 13428.214
Root Mean Square Error of Approximation:
RMSEA 0.107
90 Percent confidence interval - lower 0.099
90 Percent confidence interval - upper 0.115
P-value H_0: RMSEA <= 0.050 0.000
P-value H_0: RMSEA >= 0.080 1.000
Standardized Root Mean Square Residual:
SRMR 0.119
Parameter Estimates:
Standard errors Standard
Information Expected
Information saturated (h1) model Structured
Latent Variables:
Estimate Std.Err z-value P(>|z|)
Happiness =~
happy4 1.000
happy3 -4.299 3.529 -1.218 0.223
happy2 -6.668 5.428 -1.229 0.219
happy1 -6.874 5.596 -1.229 0.219
Agreeableness =~
personality20 1.000
personality15 -0.955 0.754 -1.267 0.205
personality10 -4.410 2.423 -1.820 0.069
personality5 -4.034 2.211 -1.824 0.068
Openness =~
personality19 1.000
personality14 0.722 0.158 4.571 0.000
personality9 -0.200 0.100 -2.005 0.045
personality4 -0.088 0.101 -0.873 0.383
Neuroticism =~
personality18 1.000
personality13 -0.508 0.144 -3.530 0.000
personality8 -0.798 0.172 -4.651 0.000
personality3 -0.354 0.133 -2.664 0.008
Conscientiousness =~
personality17 1.000
personality12 -0.523 0.180 -2.911 0.004
personality7 -0.455 0.189 -2.412 0.016
personality2 1.055 0.241 4.378 0.000
Extroversion =~
personality16 1.000
personality11 0.632 0.151 4.181 0.000
personality6 -0.559 0.138 -4.038 0.000
personality1 -0.558 0.134 -4.170 0.000
Regressions:
Estimate Std.Err z-value P(>|z|)
friends.Z1 ~
Extroversion -0.383 0.457 -0.838 0.402
friends.Z2 ~
Extroversion -0.586 0.491 -1.192 0.233
friends.Z1 ~
Conscientisnss -0.148 1.023 -0.144 0.885
friends.Z2 ~
Conscientisnss 0.503 1.048 0.480 0.631
friends.Z1 ~
Neuroticism -0.004 0.718 -0.006 0.995
friends.Z2 ~
Neuroticism 1.780 0.898 1.982 0.048
friends.Z1 ~
Openness 0.352 0.466 0.756 0.450
friends.Z2 ~
Openness -1.003 0.559 -1.794 0.073
friends.Z1 ~
Agreeableness 0.961 2.930 0.328 0.743
friends.Z2 ~
Agreeableness -2.654 3.260 -0.814 0.416
Happiness ~
friends.Z1 -0.016 0.013 -1.165 0.244
friends.Z2 -0.002 0.005 -0.394 0.693
wechat.Z1 0.019 0.017 1.146 0.252
wechat.Z2 -0.001 0.006 -0.192 0.848
Covariances:
Estimate Std.Err z-value P(>|z|)
Agreeableness ~~
Openness 0.018 0.019 0.965 0.334
Neuroticism 0.044 0.029 1.538 0.124
Conscientisnss -0.075 0.043 -1.727 0.084
Extroversion -0.011 0.020 -0.553 0.580
Openness ~~
Neuroticism 0.346 0.075 4.596 0.000
Conscientisnss -0.141 0.063 -2.233 0.026
Extroversion 0.085 0.080 1.063 0.288
Neuroticism ~~
Conscientisnss -0.150 0.063 -2.391 0.017
Extroversion 0.212 0.081 2.605 0.009
Conscientiousness ~~
Extroversion 0.154 0.074 2.073 0.038
Variances:
Estimate Std.Err z-value P(>|z|)
.happy4 2.702 0.298 9.065 0.000
.happy3 1.218 0.146 8.332 0.000
.happy2 0.569 0.137 4.141 0.000
.happy1 0.522 0.142 3.678 0.000
.personality20 1.103 0.123 8.968 0.000
.personality15 1.208 0.134 8.987 0.000
.personality10 0.511 0.135 3.773 0.000
.personality5 0.786 0.135 5.806 0.000
.personality19 0.184 0.139 1.326 0.185
.personality14 0.710 0.107 6.662 0.000
.personality9 0.858 0.095 9.013 0.000
.personality4 0.964 0.106 9.072 0.000
.personality18 0.484 0.104 4.635 0.000
.personality13 0.929 0.109 8.529 0.000
.personality8 0.963 0.125 7.720 0.000
.personality3 0.899 0.102 8.809 0.000
.personality17 0.568 0.102 5.555 0.000
.personality12 1.055 0.123 8.600 0.000
.personality7 1.270 0.145 8.781 0.000
.personality2 1.065 0.151 7.046 0.000
.personality16 0.641 0.167 3.831 0.000
.personality11 1.120 0.144 7.796 0.000
.personality6 1.011 0.127 7.983 0.000
.personality1 0.883 0.113 7.813 0.000
.friends.Z1 9.034 1.006 8.984 0.000
.friends.Z2 7.746 1.033 7.497 0.000
.Happiness 0.025 0.041 0.615 0.538
Agreeableness 0.034 0.036 0.934 0.350
Openness 0.712 0.168 4.234 0.000
Neuroticism 0.508 0.131 3.880 0.000
Conscientisnss 0.387 0.117 3.310 0.001
Extroversion 0.798 0.208 3.842 0.000The path diagram is given below: