Node based analysis with network statistics
The function sem.net can be used to fit a SEM model with network data using node statistics as variables. User-specified network statistics will be calculated and used as variables instead of the networks themselves in the SEM.
The following choices of network statistics can be used:
degree: Degree is a centrality measure that counts actors/nodes a specific node is connected to.betweenness: Betweenness is a centrality measure that counts how many shortest path an actor is crossed by through a random choice. It measures how much an individual control the spread of information.closeness: Closeness is a measure of how efficiently a node spreads information and can be calculated by the average inverse distance from a node to all other nodes.evcent: The eigenvector centrality is a measure of transitive influence of each node, meaning that a node with high eigenvector centrality tends to connect with other nodes with high eigenvector centrality (Ruhnau, 2000).stresscent: Stress centrality is similar to betweenness centrality as it also measures the control of spread. However, while betweenness centrality measures through a random fraction of shortest paths, stress centrality takes into account all shortest paths (Szczepanski et al., 2012).infocent: Information centrality is defined as the reduction in network efficiency if a target node is removed. It is a measure of node effectiveness in spreading information (Latora and Marchiori, 2007).ivi: Integrated value of influence is a measure that combines different centrality measures (Salavaty et al., 2020a)hubeness.score: Hubeness score is a component of IVI and measures a node’s influence in its surrounding environment.spreading.score: Spreading score is another component of IVI and measures a node’s spreading potential.clusterRank: Cluster rank is a measure of clustering that takes into account a node, its neighbors, and their clustering coefficients.
Simulated Data Example
To begin with, a random simulated dataset can be used to demonstrate the usage of the node-based network statistics approach. The code below generate a simulated network net with four non-network covariates x1 - x4 which loads on two latent variables lv1, lv2.
set.seed(100)
nsamp = 100 # sample size
net <- ifelse(matrix(rnorm(nsamp^2), nsamp, nsamp) > 1, 1, 0) # simulate network
mean(net) # density of simulated network
# simulate non-network variables
lv1 <- rnorm(nsamp)
lv2 <- rnorm(nsamp)
nonnet <- data.frame(x1 = lv1*0.5 + rnorm(nsamp),
x2 = lv1*0.8 + rnorm(nsamp),
x3 = lv2*0.5 + rnorm(nsamp),
x4 = lv2*0.8 + rnorm(nsamp))With the simulated data, we can define a model string with lavaan syntax that specifies the measurement model as well as the relationship between the network and the non-network variables. In this case, we are using net as a mediator between the two latent variables. Since data are generated randomly, the effects should be small overall.
model <-'
lv1 =~ x1 + x2
lv2 =~ x3 + x4
net ~ lv2
lv1 ~ net + lv2
'Arguments passed to the sem.net function includes the model, the dataset, and the network statistics of interest. Note that data here should be a list with two elements, one being the named list of all network variables and one being the dataframe containing non-network variables. A summary function can be used to look at the output, and the function path.networksem can be used to look at mediation effects.
data = list(network = list(net = net), nonnetwork = nonnet)
set.seed(100)
res <- sem.net(model = model, data = data, netstats = c('degree'))
summary(res)
path.networksem(res, "lv2", c("net.degree"), "lv1")The output of should look like the following.
> summary(res)
The SEM output:
lavaan 0.6.15 ended normally after 54 iterations
Estimator ML
Optimization method NLMINB
Number of model parameters 12
Number of observations 100
Model Test User Model:
Test statistic 1.230
Degrees of freedom 3
P-value (Chi-square) 0.746
Model Test Baseline Model:
Test statistic 24.987
Degrees of freedom 10
P-value 0.005
User Model versus Baseline Model:
Comparative Fit Index (CFI) 1.000
Tucker-Lewis Index (TLI) 1.394
Loglikelihood and Information Criteria:
Loglikelihood user model (H0) -913.294
Loglikelihood unrestricted model (H1) -912.679
Akaike (AIC) 1850.588
Bayesian (BIC) 1881.850
Sample-size adjusted Bayesian (SABIC) 1843.951
Root Mean Square Error of Approximation:
RMSEA 0.000
90 Percent confidence interval - lower 0.000
90 Percent confidence interval - upper 0.118
P-value H_0: RMSEA <= 0.050 0.810
P-value H_0: RMSEA >= 0.080 0.120
Standardized Root Mean Square Residual:
SRMR 0.026
Parameter Estimates:
Standard errors Standard
Information Expected
Information saturated (h1) model Structured
Latent Variables:
Estimate Std.Err z-value P(>|z|)
lv2 =~
x4 1.000
x3 2.035 2.162 0.941 0.347
lv1 =~
x2 1.000
x1 1.056 0.789 1.338 0.181
Regressions:
Estimate Std.Err z-value P(>|z|)
lv1 ~
lv2 -0.441 0.300 -1.470 0.142
net.degree ~
lv2 -0.934 1.163 -0.804 0.422
lv1 ~
net.degree -0.011 0.020 -0.569 0.569
Variances:
Estimate Std.Err z-value P(>|z|)
.x4 1.350 0.293 4.603 0.000
.x3 0.215 0.923 0.233 0.816
.x2 1.002 0.299 3.357 0.001
.x1 1.047 0.328 3.190 0.001
.net.degree 22.292 3.164 7.046 0.000
lv2 0.214 0.249 0.860 0.390
.lv1 0.302 0.264 1.142 0.253
> path.networksem(res, "lv2", c("net.degree"), "lv1")
predictor mediator outcome apath bpath indirect indirect_se indirect_z
1 lv2 net.degree lv1 -0.934393 -0.01126621 0.01052707 1.086552 0.009688509Empirical Data Example
Using the friendship network data, a model with 5 personality traits and two networks' effect on happiness can be fitted using the code below. In this case, degree, betweenness, closeness are used as network statistics.
# load data
load("data/cf_data_book.RData") ## load the list cf_data
## data - non-network variables
non_network <- as.data.frame(cf_data$cf_nodal_cov)
dim(non_network)
## network - network variables (friends network and wechat network)
## note that the names of the networks are used in model specification
network <- list()
network$friends <- cf_data$cf_friend_network
network$wechat <- cf_data$cf_wetchat_network
model <-'
Extroversion =~ personality1 + personality6
+ personality11 + personality16
Conscientiousness =~ personality2 + personality7
+ personality12 + personality17
Neuroticism =~ personality3 + personality8
+ personality13 + personality18
Openness =~ personality4 + personality9
+ personality14 + personality19
Agreeableness =~ personality5 + personality10 +
personality15 + personality20
Happiness =~ happy1 + happy2 + happy3 + happy4
friends ~ Extroversion + Conscientiousness + Neuroticism +
Openness + Agreeableness
Happiness ~ friends + wechat
'
## run sem.net
data = list(
nonnetwork = non_network,
network = network
)
set.seed(100)
res <- sem.net(model=model, data=data,
netstats=c("degree", "betweenness", "closeness"),
netstats.rescale = T,
netstats.options=list("degree"=list("cmode"="freeman")))
## results
summary(res)The output of the analysis is given below:
lavaan 0.6-18 ended normally after 453 iterations
Estimator ML
Optimization method NLMINB
Number of model parameters 82
Number of observations 165
Model Test User Model:
Test statistic 844.769
Degrees of freedom 377
P-value (Chi-square) 0.000
Model Test Baseline Model:
Test statistic 1795.826
Degrees of freedom 432
P-value 0.000
User Model versus Baseline Model:
Comparative Fit Index (CFI) 0.657
Tucker-Lewis Index (TLI) 0.607
Loglikelihood and Information Criteria:
Loglikelihood user model (H0) -6286.542
Loglikelihood unrestricted model (H1) -5864.157
Akaike (AIC) 12737.084
Bayesian (BIC) 12991.771
Sample-size adjusted Bayesian (SABIC) 12732.159
Root Mean Square Error of Approximation:
RMSEA 0.087
90 Percent confidence interval - lower 0.079
90 Percent confidence interval - upper 0.095
P-value H_0: RMSEA <= 0.050 0.000
P-value H_0: RMSEA >= 0.080 0.922
Standardized Root Mean Square Residual:
SRMR 0.116
Parameter Estimates:
Standard errors Standard
Information Expected
Information saturated (h1) model Structured
Latent Variables:
Estimate Std.Err z-value P(>|z|)
Happiness =~
happy4 1.000
happy3 -4.283 3.684 -1.162 0.245
happy2 -6.682 5.698 -1.173 0.241
happy1 -6.955 5.932 -1.172 0.241
Agreeableness =~
personality20 1.000
personality15 -1.200 0.905 -1.326 0.185
personality10 -4.293 2.506 -1.713 0.087
personality5 -4.462 2.606 -1.712 0.087
Openness =~
personality19 1.000
personality14 0.784 0.165 4.748 0.000
personality9 -0.224 0.106 -2.110 0.035
personality4 -0.097 0.108 -0.898 0.369
Neuroticism =~
personality18 1.000
personality13 -0.532 0.148 -3.603 0.000
personality8 -0.808 0.176 -4.602 0.000
personality3 -0.378 0.136 -2.778 0.005
Conscientiousness =~
personality17 1.000
personality12 -0.693 0.214 -3.235 0.001
personality7 -0.508 0.219 -2.319 0.020
personality2 1.108 0.265 4.187 0.000
Extroversion =~
personality16 1.000
personality11 0.609 0.136 4.493 0.000
personality6 -0.508 0.123 -4.116 0.000
personality1 -0.521 0.119 -4.377 0.000
Regressions:
Estimate Std.Err z-value P(>|z|)
friends.degree ~
Extroversion 2.355 1.126 2.091 0.037
friends.betweenness ~
Extroversion 2.119 1.048 2.023 0.043
friends.closeness ~
Extroversion 2.175 1.026 2.119 0.034
friends.degree ~
Conscientisnss -8.447 5.060 -1.670 0.095
friends.betweenness ~
Conscientisnss -7.827 4.706 -1.663 0.096
friends.closeness ~
Conscientisnss -7.720 4.609 -1.675 0.094
friends.degree ~
Neuroticism -1.282 1.364 -0.940 0.347
friends.betweenness ~
Neuroticism -1.252 1.272 -0.985 0.325
friends.closeness ~
Neuroticism -1.324 1.248 -1.061 0.289
friends.degree ~
Openness -1.355 1.483 -0.914 0.361
friends.betweenness ~
Openness -1.204 1.377 -0.875 0.382
friends.closeness ~
Openness -1.162 1.348 -0.862 0.389
friends.degree ~
Agreeableness -16.541 15.253 -1.084 0.278
friends.betweenness ~
Agreeableness -15.697 14.299 -1.098 0.272
friends.closeness ~
Agreeableness -14.400 13.668 -1.054 0.292
Happiness ~
friends.degree -0.047 0.051 -0.931 0.352
frinds.btwnnss 0.007 0.025 0.292 0.771
friends.clsnss 0.062 0.059 1.045 0.296
wechat.degree 0.013 0.037 0.351 0.725
wechat.btwnnss 0.050 0.049 1.027 0.305
wechat.closnss -0.064 0.060 -1.063 0.288
Covariances:
Estimate Std.Err z-value P(>|z|)
Agreeableness ~~
Openness 0.015 0.018 0.866 0.386
Neuroticism 0.043 0.029 1.479 0.139
Conscientisnss -0.072 0.044 -1.643 0.100
Extroversion -0.011 0.020 -0.554 0.579
Openness ~~
Neuroticism 0.330 0.074 4.446 0.000
Conscientisnss -0.166 0.059 -2.806 0.005
Extroversion 0.089 0.080 1.111 0.266
Neuroticism ~~
Conscientisnss -0.153 0.058 -2.648 0.008
Extroversion 0.212 0.082 2.588 0.010
Conscientiousness ~~
Extroversion 0.174 0.070 2.490 0.013
Variances:
Estimate Std.Err z-value P(>|z|)
.happy4 2.702 0.298 9.066 0.000
.happy3 1.226 0.147 8.353 0.000
.happy2 0.577 0.139 4.146 0.000
.happy1 0.507 0.145 3.496 0.000
.personality20 1.107 0.123 8.979 0.000
.personality15 1.195 0.134 8.945 0.000
.personality10 0.617 0.115 5.359 0.000
.personality5 0.742 0.130 5.705 0.000
.personality19 0.244 0.125 1.948 0.051
.personality14 0.680 0.107 6.372 0.000
.personality9 0.854 0.095 8.982 0.000
.personality4 0.963 0.106 9.067 0.000
.personality18 0.498 0.104 4.790 0.000
.personality13 0.920 0.109 8.469 0.000
.personality8 0.965 0.125 7.694 0.000
.personality3 0.893 0.102 8.768 0.000
.personality17 0.707 0.088 8.051 0.000
.personality12 1.042 0.119 8.753 0.000
.personality7 1.286 0.144 8.940 0.000
.personality2 1.193 0.143 8.337 0.000
.personality16 0.595 0.152 3.917 0.000
.personality11 1.125 0.140 8.023 0.000
.personality6 1.043 0.126 8.305 0.000
.personality1 0.902 0.111 8.122 0.000
.friends.degree 0.074 0.026 2.872 0.004
.frinds.btwnnss 0.236 0.034 6.912 0.000
.friends.clsnss 0.170 0.029 5.849 0.000
.Happiness 0.024 0.040 0.587 0.557
Agreeableness 0.030 0.034 0.874 0.382
Openness 0.652 0.155 4.209 0.000
Neuroticism 0.495 0.129 3.822 0.000
Conscientisnss 0.248 0.082 3.038 0.002
Extroversion 0.843 0.199 4.240 0.000
The multiple mediation from Agreeableness to friendship network to Happiness can be calculated using the following code.
> path.networksem(res, 'Agreeableness',
c('friends.degree', 'friends.betweenness', 'friends.closeness'),
'Happiness')
predictor mediator outcome apath bpath indirect
1 Agreeableness friends.degree Happiness -16.54130 -0.047133471 0.7796491
2 Agreeableness friends.betweenness Happiness -15.69767 0.007403778 -0.1162220
3 Agreeableness friends.closeness Happiness -14.40081 0.061957757 -0.8922416
indirect_se indirect_z
1 252.3110 0.0030900323
2 224.4727 -0.0005177557
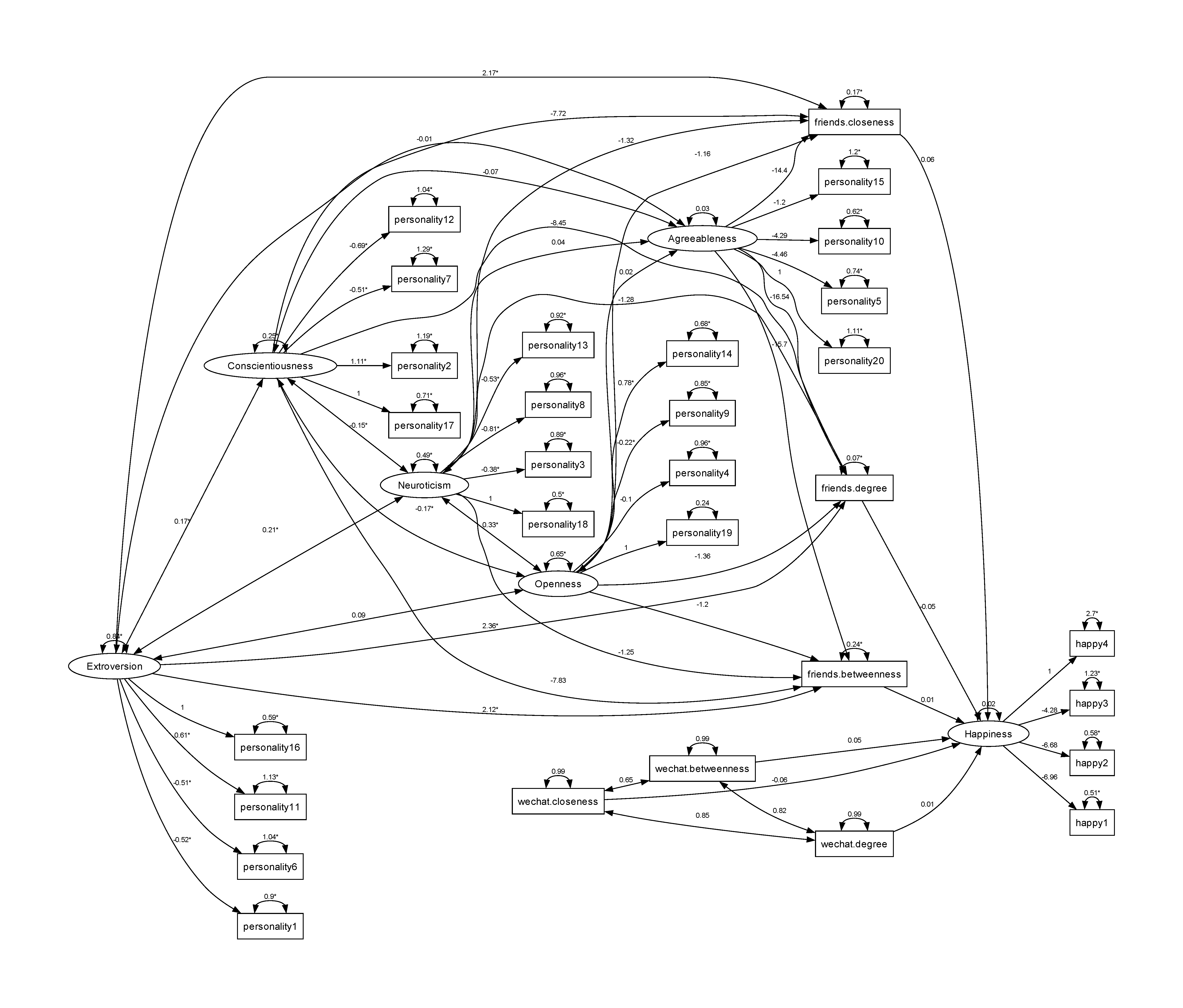
3 196.8378 -0.0045328765The model used here is shown in the diagram below. The model has the following features:
- We use two networks - friendship and WeChat networks.
- Three network statistics are used - degree, closeness, and betweenness.
- Friendship network is used as mediators.