Edge based analysis with latent space model
The R function sem.net.edge.lsm can be used to conduct edge based analysis with latent space model. In this case, the latent distance between each pair of individuals is used along with the transformed non-network covariates in SEM.
Simulated Data Example
To begin with, a random simulated dataset can be used to demonstrate the usage of the node-based network statistics approach. The code below generate a simulated network net with four non-network covariates x1 - x4 which loads on two latent variables lv1, lv2.
set.seed(10)
nsamp = 50
lv1 <- rnorm(nsamp)
net <- ifelse(matrix(rnorm(nsamp^2) , nsamp, nsamp) > 1, 1, 0)
lv2 <- rnorm(nsamp)
nonnet <- data.frame(x1 = lv1*0.5 + rnorm(nsamp),
x2 = lv1*0.8 + rnorm(nsamp),
x3 = lv2*0.5 + rnorm(nsamp),
x4 = lv2*0.8 + rnorm(nsamp))With the simulated data, we can define a model string with lavaan syntax that specifies the measurement model as well as the relationship between the network and the non-network variables. In this case, we are using net as a mediator between the two latent variables. Since data are generated randomly, the effects should be small overall.
model <-'
lv1 =~ x1 + x2
lv2 =~ x3 + x4
net ~ lv1
lv2 ~ net
'Arguments passed to the sem.net.edge.lsm function includes the model, the dataset, and the latent dimensions. Note that data here should be a list with two elements, one being the named list of all network variables and one being the dataframe containing non-network variables. A summary function can be used to look at the output.
data = list(network = list(net = net), nonnetwork = nonnet)
set.seed(100)
res <- sem.net.edge.lsm(model = model, data = data, latent.dim = 1)
summary(res)
path.networksem(res, 'lv2', c('net.dists'), 'lv1')The output is shown below:
Model Fit InformationSEM Test statistics: 492.628 on 4 df with p-value: 0
network 1 LSM BIC: 2244.546
========================================
========================================
The SEM output:
lavaan 0.6.15 ended normally after 29 iterations
Estimator ML
Optimization method NLMINB
Number of model parameters 11
Number of observations 2500
Model Test User Model:
Test statistic 492.628
Degrees of freedom 4
P-value (Chi-square) 0.000
Model Test Baseline Model:
Test statistic 958.550
Degrees of freedom 10
P-value 0.000
User Model versus Baseline Model:
Comparative Fit Index (CFI) 0.485
Tucker-Lewis Index (TLI) -0.288
Loglikelihood and Information Criteria:
Loglikelihood user model (H0) -22209.465
Loglikelihood unrestricted model (H1) NA
Akaike (AIC) 44440.930
Bayesian (BIC) 44504.994
Sample-size adjusted Bayesian (SABIC) 44470.045
Root Mean Square Error of Approximation:
RMSEA 0.221
90 Percent confidence interval - lower 0.205
90 Percent confidence interval - upper 0.238
P-value H_0: RMSEA <= 0.050 0.000
P-value H_0: RMSEA >= 0.080 1.000
Standardized Root Mean Square Residual:
SRMR 0.109
Parameter Estimates:
Standard errors Standard
Information Expected
Information saturated (h1) model Structured
Latent Variables:
Estimate Std.Err z-value P(>|z|)
lv2 =~
x4 1.000
x3 0.976 NA
lv1 =~
x2 1.000
x1 0.642 NA
Regressions:
Estimate Std.Err z-value P(>|z|)
net.dists ~
lv1 -0.000 NA
lv2 ~
net.dists -0.000 NA
Variances:
Estimate Std.Err z-value P(>|z|)
.x4 2.856 NA
.x3 1.501 NA
.x2 1.722 NA
.x1 2.490 NA
.net.dists 0.553 NA
.lv2 1.315 NA
lv1 0.715 NA
The LSM output:
==========================
Summary of model fit
==========================
Formula: network::network(data$network[[latent.network[i]]]) ~ euclidean(d = latent.dim)
<environment: 0x7fc473af4960>
Attribute: edges
Model: Bernoulli
MCMC sample of size 4000, draws are 10 iterations apart, after burnin of 10000 iterations.
Covariate coefficients posterior means:
Estimate 2.5% 97.5% 2*min(Pr(>0),Pr(<0))
(Intercept) -0.67923 -0.83587 -0.5504 < 2.2e-16 ***
---
Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1
Overall BIC: 2244.546
Likelihood BIC: 2184.507
Latent space/clustering BIC: 60.03918
Covariate coefficients MKL:
Estimate
(Intercept) -1.117408Empirical Data Example
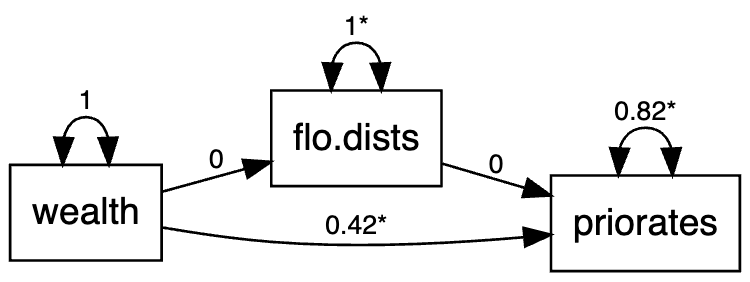
When embedding the LSM into the edge-based approach, one thing that needs to be considered is whether to model covariates predicting the social networks in the LSM framework or in the SEM framework. This is only a concern in the edge-based model since covariates need to be edge-based as well if using the LSM method, and it defies the purpose of simplicity if we consider the LSM in the actor-based approach. In this example, we will accommodate the covariates in the LSM framework within the edge-based approach. The dataset used in this example is the Florentine marriage dataset. The model is quite simple as shown below. Essentially, the observed marriage network is hypothesized to be based not only on the latent positions, but also on the non-network variable of wealth. Additionally, priorates is viewed as a predictor of the distance between latent positrons of the marriage networks.
load("data/flomarriage.RData")
network <- list()
network$flo <- flomarriage.network
nonnetwork <- flomarriage.nonnetwork
model <- '
flo ~ wealth
priorates ~ flo + wealth
'When fitting the model using the sem.net.edge.lsm function, the argument type and latent.dim are needed. Here, although the marriage network contains binary edges, the ordered argument is not needed since only the continuous latent distances will be used in the SEM.
data = list(network=network, nonnetwork=nonnetwork)
set.seed(100)
res <- sem.net.edge.lsm(model=model,data=data, type = "difference", latent.dim = 2, netstats.rescale = T, data.rescale = T)
## results
summary(res)In this model, the latentnet package is first used to estimate the LSM with the covariate of wealth. Then, the resulting latent positions of the marriage network, taking apart the effect of wealth, is hypothesized to be influenced by priorates and the effect is estimated through lavaan. Thus, the latent distances of the marriage network acts like a mediator between priorates and the observed network. The resulting estimates from both the SEM component and the LSM component are shown below.
Model Fit InformationSEM Test statistics: 0 on 0 df with p-value: NA
network 1 LSM BIC: 259.7975
========================================
========================================
The SEM output:
lavaan 0.6.15 ended normally after 6 iterations
Estimator ML
Optimization method NLMINB
Number of model parameters 5
Number of observations 256
Model Test User Model:
Test statistic 0.000
Degrees of freedom 0
Model Test Baseline Model:
Test statistic 50.126
Degrees of freedom 3
P-value 0.000
User Model versus Baseline Model:
Comparative Fit Index (CFI) 1.000
Tucker-Lewis Index (TLI) 1.000
Loglikelihood and Information Criteria:
Loglikelihood user model (H0) -700.431
Loglikelihood unrestricted model (H1) -700.431
Akaike (AIC) 1410.863
Bayesian (BIC) 1428.589
Sample-size adjusted Bayesian (SABIC) 1412.737
Root Mean Square Error of Approximation:
RMSEA 0.000
90 Percent confidence interval - lower 0.000
90 Percent confidence interval - upper 0.000
P-value H_0: RMSEA <= 0.050 NA
P-value H_0: RMSEA >= 0.080 NA
Standardized Root Mean Square Residual:
SRMR 0.000
Parameter Estimates:
Standard errors Standard
Information Expected
Information saturated (h1) model Structured
Regressions:
Estimate Std.Err z-value P(>|z|)
priorates ~
wealth 0.422 0.057 7.441 0.000
flo.dists ~
wealth 0.000 0.063 0.000 1.000
priorates ~
flo.dists -0.000 0.057 -0.000 1.000
Variances:
Estimate Std.Err z-value P(>|z|)
.priorates 0.819 0.072 11.314 0.000
.flo.dists 0.996 0.088 11.314 0.000
The LSM output:
==========================
Summary of model fit
==========================
Formula: network::network(data$network[[latent.network[i]]]) ~ euclidean(d = latent.dim)
<environment: 0x7fc434ed5160>
Attribute: edges
Model: Bernoulli
MCMC sample of size 4000, draws are 10 iterations apart, after burnin of 10000 iterations.
Covariate coefficients posterior means:
Estimate 2.5% 97.5% 2*min(Pr(>0),Pr(<0))
(Intercept) 5.0133 2.5627 7.9665 < 2.2e-16 ***
---
Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1
Overall BIC: 259.7975
Likelihood BIC: 85.53086
Latent space/clustering BIC: 174.2666
Covariate coefficients MKL:
Estimate
(Intercept) 2.861026To look at indirect effects, the following code can be used.
> path.networksem(res, "wealth","flo.dists", "priorates")
predictor mediator outcome apath bpath indirect
1 wealth flo.dists priorates 2.976241e-21 -4.047181e-22 -1.204539e-42
indirect_se indirect_z
1 1.874237e-22 -6.42682e-21The model is shown in this diagram below.